What is HIRA / Hazard Indetifciation and Risk Assessment ?
HIRA itself a self explnatory word , HIRA means, identification of all type of hazard in as Physical hazard, chemical hazard , bio hazard process, mechanical hazard pertinanat to operation and activity with reference to machine operation, workplace design , workplace condition, manual Operation, machine and equipment design aspect, site layout , change , modification and expansion , different types of utility service etc. all these identified hazard to be listed in prescribed Format.
After Hazard identification , Risk assessment is done for all hazard and scale the risk as per pre-determind risk matrix by determimng the Probability of occurrence and severity of undesired event . The Entire procedure as follow:
What should we konw before conducting HIRA ?
Risk: Risk is the chance or probability that a person will be harmed or experience an adverse health effect if exposed to a hazard. It may also apply to situations with property or equipment loss, or harmful effect on the environment. The combination of frequency, or probability of occurrence of a hazard and consequence of a specified hazardous event.
Corrective Action: The corrective action taken to eliminate the cause of an existing nonconformity, defect of other undesirable situation in order to prevent recurrence.
Preventive Action: The action taken to eliminate the cause of a potential nonconformity, defect or other undesirable situation in order to prevent occurrence.
Hazard: A source or a situation with a potential to cause harm in term of human injury or ill health, damage to property, damage to the environment or a combination of these.
Hazard Identification: The process of recognizing a hazard in existence and defining its characteristic / impact.
Risk Assessment: Risk assessment is a term used to describe the overall process or method where you, identify hazard and risk factors that have the potential to cause harm (hazard identification). Analyse and evaluate the risk associated with that hazard (risk analysis and risk evaluation). Determine appropriate ways to eliminate the hazard or control the risk when the hazard can be eliminated (risk control).
Severity: Degree or extent of injury or harm caused by hazard or as a result of an accident / incident.
Likelihood: Probability or frequency of a hazardous event occurring.
Risk Evaluation: The process of comparing an estimated risk against given risk criteria to determine the significance of the risk.
What is to be covered to be under HIRA or What Activity or operation should be consider while conducting HIRA
List of all work activities whether is routine or non-routine, as department/area/process-wise. The major activities are as follow
- Receipt , issuance and Storage of Raw Materials
- Production and Packing.
- Storage of Finished Products
- Effluent TreatmentWaste management
- General Administration
- Repair and Maintenance activity (Internal and External Services)
- QC Analysis
- Projects
- Internal Material transportation.
- Dispatch loading.
- Receipt, issuance and storage of Engg. Item.
- Admin operation like Canteene, Gardening etc.
- utility Operation
- External vendor activity or operation at site
- Civil and Construction work
- Repairing and Maintenance Work
Services: These are supporting functions and facilities at the workplace, whether provided by organization or others.
- Transport services
- Utility services like D.G. Set, Compressor, etc.
- Water supply services
- Security services
- Green belt maintenance
- Contract Activities for labor, repair and maintenance, testing and analysis
- Calibration, Monitoring and measurement work.
A. Hazard Identification
What are the reliable sources to get over information about Hazard in factory Premises?
Following are some significant source to get information about hazard:-
- OHS review of all activities and operations performing at site.
- Regulatory and statutory requirements.
- Interviews with functional staff.
- National and international standard relevant to industry specific and Generic Indian Standard 15656:2006.
- Incident, Accident and near miss Record.
- Safety committee meeting Minutes.
- Suggestion and recommendation of employee, worker and Visitors.
- Third party Audit Report.
- Circular, Notice , Guideline issued by regulatory and statutory authorities.
- Safety Inspection Reports.
- Operation and Maintenance Manual of Equipment.
- Dossier of Equipment and machineries.
- Contract agreement of contractor (term and condition)Feedback by customer.
What Tools can be used for conducting HIRA?
- Checklists for Qualitative HIRA
- Job Safety analysis
- Pre Startup Safety Review etc.
- Hazard and Operability Study .
- Fault Tree Analysis,
- Event tree Analysis.
- Failure mode and effect Analysis.
- Layer of Protection Analysis
- Quantitative Risk Analysis and simulation etc.
- Appropriate for process, Activity and any modification, changes.Various software tools intended to quantify the Risk onsite or offsite.
B. Risk Assessment
Following are step for Risk Assessment :
- Identifying the existing risk control measures.
- Assessing the potential severity of the hazard
- Determining the likelihood of occurrence
- Assessing the risk level based on severity and likelihood
Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment Chart
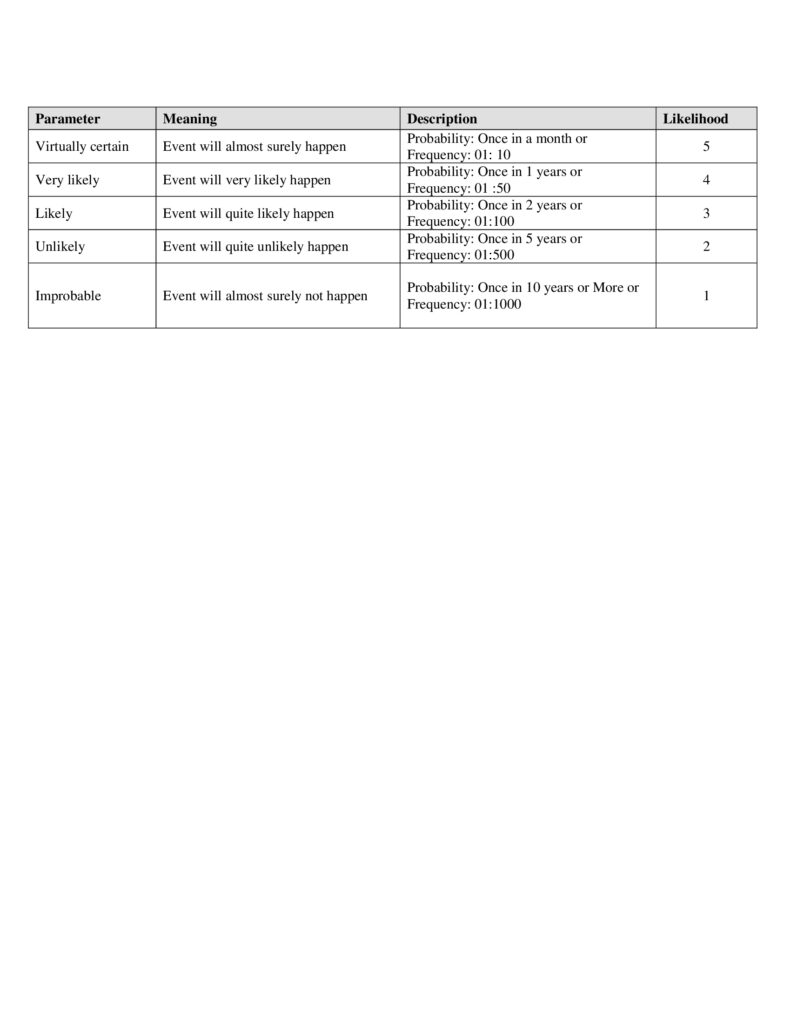
In order to quantify the OH&S Risk following terms were defined
Probability of Occurrence [P]: A probability category is assigned to each hazard to provide a qualitative ranking of its probability of occurrence. Likelihood/probability will be derived on expertise knowledge and actual experience or perception considering below table: The likelihood /probability of a particular risk will be considered after evaluating effectiveness of existing Controls.